View Project
Establishment of field disease diagnostic laboratory for servicing and capacity building of marginalized society in brackishwater aquaculture
Status: New
Lab/Organization
| Name & address of the Laboratory/Organization | ICAR-Central Institute Brackishwater Aquaculture, Chennai | |
| Website address | https://ciba.icar.gov.in | |
| Affiliated to which Department/Ministry | Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) | |
| CSR Registration Number | GSR 776(E) | |
| Registration under 12A | ||
| Registration under 80G | ||
| Name of the CSR Nodal | Dr. R. Geetha | |
| Contact information of CSR Nodal | 7299201687, geetha.r@icar.gov.in | |
| Principal Investigator | Dr.R.Ananda Raja, ananda.raja@icar.gov.in https://ciba.icar.gov.in |
|
| Co- Principal Investigator (Co-PI) | Dr.M.Kumaran, m.kumaran@icar.gov.in | |
Project Detail
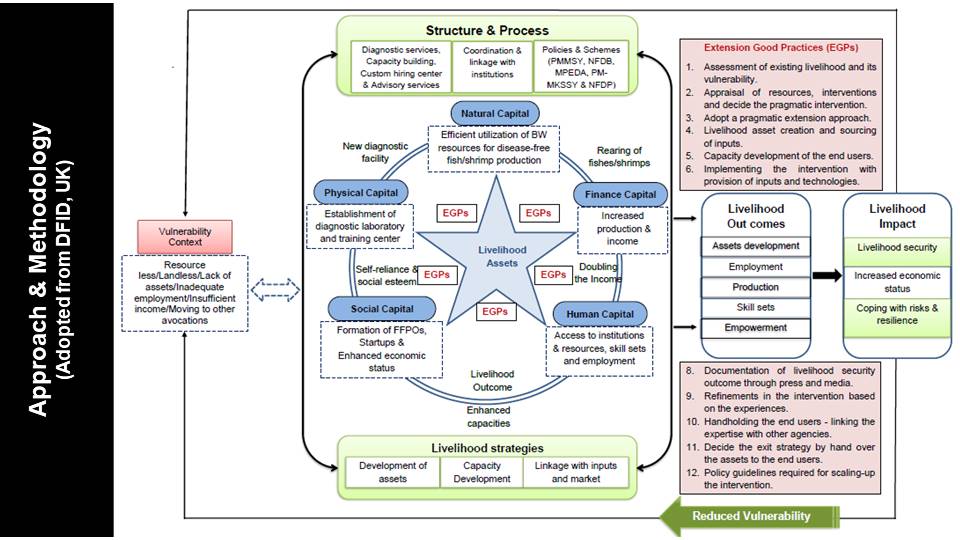
| Objective on the basis of need | To establish a field diagnostic laboratory for providing free diagnostic services to the brackishwate aquaculture farmers. To develop diagnostic expertise among the rural educated youths for improving their livelihoo options in a self-sustained manner and serving the industry. To assess the health of aquatic animals for the bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic and other disease of commercial importance following standard diagnostic methods. To extend full-fledged diagnostic support and services to the aquaculture farmers in terms o microbiological and molecular diagnosis of diseases in brackishwater aquatic organisms. To study the socio-economic upliftment of the community after the execution of this project |
| Executive summary of the proposed project (In 250 words) | Shrimp aquaculture is a flourishing food-producing sector and is an important economic activity in many shrimp farming nations. The total quantity of marine products exported from India during 2023-24 was 1.78 MMT with a value of Indian rupees (INR) 60523.89 crores, of which the frozen shrimp contributed a major share of 0.72 MMT with a value of INR 40013.54 crores. The three crustaceans P. vannamei, P. monodon, and Macrobrachium rosenbergii are the sole contributors to the Indian shrimp production. P. vannamei is the dominant species, followed by P. monodon and M. rosenbergii. In India, 108526.27 ha are under the culture of P. vannamei, and 58196 ha are under the culture of P. monodon. Nagapattinam is one of the most important district contributing maximum from Tamil Nadu with more than 900 shrimp farms widespread in an area of 5000 ha. Once the locally harvested shrimp is mixed with common pool and detected as positive for any notified pathogen, the entire consignment likely to get rejected. In order to avoid such scenario, it is essential to screen at the field level before the harvest reaches the common pool. The most importantly, the educated resource less youths from the marginalized society shall be trained for disease diagnostics in brackishwater aquaculture and make them self-reliant with knowledge and skill. Hence, this project is proposed for field level disease diagnostic facility as an early warning mechanism and capacity building centre as an employment generator for youths in brackishwater aquaculture. |
| Technology Readiness Level (If not a new project but an advancement of existing know how) | Disease diagnostic technologies in brackishwater aquaculture will be applied with the scientific and technical expertise available in ICAR-CIBA following the different technologies developed by ICAR-CIBA and Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals (the Aquatic Manual) published by the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). |
| Outomes or Deliverables | Since, the marginal population in this district is maximum landless laborers, any aquaculture activities can only be executed using common water bodies with the approval of local panchayats. As long as the involvement of the Government institutions and supply of free inputs are in place, this population could do aquaculture activities in common water bodies. Once, the support is withdrawn, they fail in continuing the same activities due to various socio-economic problems. Hence, any kind of skill development to the educated youths of this marginalized society will guarantee the permanent livelihood option to them. And the educated youths can self-sustain with the learned skills by either setting up some small scale laboratories and/or providing technical expertise to the well-established brackishwater aquaculture firms, rather than being as laborers. The facility can also serve as a field level disease screening laboratory to generate income for its self sustainability. |
| Project aligned with which most relevant UN SDGs | Goal 3 - Good Health & Well-Being |
| Duration (In years) | 3 |
| Expected Impact | The marginal population in the Nagapattinam district is the highest of 31.54% against the state percentage of 20.01%. Having good literacy but lack of land resources, the population in the district has been serving as the laborers in different fields. Whatsoever technological aquaculture based interventions are implemented with these landless laborers, they are left in the state of poverty once the inputs are withdrawn. Hence, it is another approach to select the educated and unemployed youths of this marginalized society, and teach and train them with basic aquaculture diagnostic skills. This will be a kick-start opportunity for educated and unemployed youths from the marginalized society, to become an expert over the years of involvement and experience. |
| Implementation model (self- implemented/ outsourced partnership) | Skill Development Programme on brackishwater aquaculture by the Avanti Foundation in collaboration with ICAR-CIBA, Chennai at Andhra University campus, Visakhapatnam. |
| Total Budget (Recurring +Non-Recurring Expenses) | Rs. 9876000 (5316000+4560000) |